Blog
Section Title
Color Fastness Color fastness is the ability of a textile material, like fabric or yarn, to retain its color without fading, bleeding, or transferring when exposed to external factors such as washing...
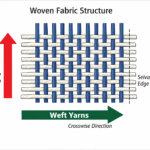
Weaving:- Weaving is a textile-making technique where two sets of threads — the warp (vertical threads) and the weft (horizontal threads) — are interlaced to create fabric. It’s one of the oldest...
In the garment industry, fabric is the primary raw material used to create clothing and textile products. It’s a flexible material made by weaving, knitting, or bonding fibers together. Fabrics...
pH pH is a scale that measures how acidic or alkaline (basic) a solution is. It ranges from 0 to 14, where 7 is neutral — like pure water. Values below 7 indicate acidity (like lemon juice), and...
Textile Dyeing: Processes and Techniques Textile dyeing is one of the most essential and transformative processes in the production of fabrics and garments. It involves the application of color to...
Needle In sewing, a needle is a slender, pointed tool used to stitch fabric, leather, or other materials together — either by hand or with a sewing machine. A sewing machine needle is a specialized...
Fusing Machine in the Garment Industry The fusing machine is typically used in the interlining process, where a thin layer of fusible material (often a type of fabric or film coated with adhesive)...
What Is Loom ? The loom is one of the most remarkable inventions in human history, a cornerstone of the textile industry that has evolved over thousands of years. From ancient handlooms to today’s...
Fabric pilling is the formation of small, fuzzy balls of fiber (pills) on the surface of a fabric due to wear and friction. It happens when loose fibers on the fabric’s surface become tangled...